Gradient is a combination of 2 or more color fills in Linear or Radial direction. There are a few ways to apply Gradient fill - via Tool Palette, Gradient Palette or (keyboard) shortcut >.
Apply Gradient via Tool Palette
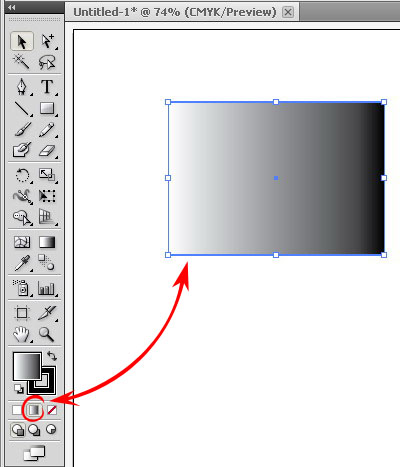
Select your artwork object, click the Gradient Fill icon as shown above.
Apply Gradient via Gradient Palette
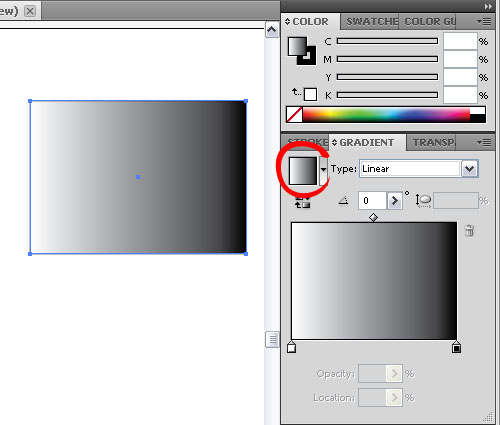
Object is selected, go to Gradient Palette, click the Gradient icon (as shown above).
Note: If the Gradient Palette is not there, open at top menu > Window > Gradient. Or keyboard shortcut is Ctrl+F9 (Win), Cmd+F9 (Mac).
Change Gradient Color
Now your artwork / object Filled with Gradient, with default black & white greyscale (1 color). We need to change this default in order to color it.
Select your object (you want to change)..
1. go to Gradient Palette, see the Gradient Slider, click the Black Slider
2. go to Color Palette, click Option (top right corner) as shown above

3. Change from (default) Greyscale to RGB (or CMYK if you need so)

4. Adjust the color, any color you like (suddenly I remember Pink Floyd song.. lol). Now your object's gradient color changed.

5. Then you need to do the same steps for the second Slider - the white gradient color.
Now you know how to change the Gradient Color of your object. Next we try to adjust the Gradient Style.
Change Gradient Style
You need to experiment yourself with these basic methods on how to modify and control your Gradient Fills on your artworks.Linear Gradient
The steps we learnt above is Linear type of gradient, and we can adjust the Slider Location to modify the effects.
Drag the Sliders and see your object gradient's effect changed.

Now change the angle direction as shown above.. try it.
Radial Gradient
Simply change the Type to Radial as shown in the image below
See your object fill color now is Radial Gradient.
There are some more extra things we can add to this Gradient Fill, but what we have learn here are just the basic of Gradient in Illustrator. We can add more colors to the gradient's object by adding more than 2 Sliders, such as rainbow colors. We can also make the gradient in different styles than this 2 basic types, but that would be more complicated for newbie.. we can try it later hopefully ☺
Note:
This tutorial is based on Adobe Illustrator CS5. Legacy version (CS4 and below), newer version (CS6 and CC) might be differ than images shown and methods in this post. I'm trying to make it as compatible as possible for any version. Therefore some new & extra features or technics that not available in previous versions might not be shown here to avoid some users confusing.









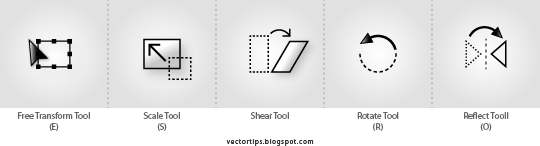
 (shortcut E), cursor will change, drag corner to freely scale the size.
(shortcut E), cursor will change, drag corner to freely scale the size.
 (dialog box appear), set the % value.
(dialog box appear), set the % value.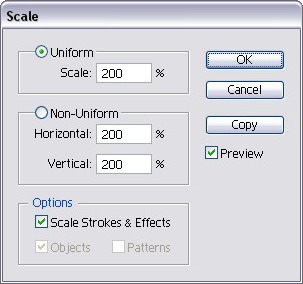
 Hold Shift to rotate consistently 45° or 90° to the left or right.
Hold Shift to rotate consistently 45° or 90° to the left or right. (dialog box appear), set the ° value.
(dialog box appear), set the ° value.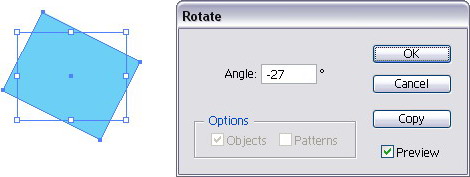
 (dialog box appear), set Hor. & Ver. value, click OK.
(dialog box appear), set Hor. & Ver. value, click OK.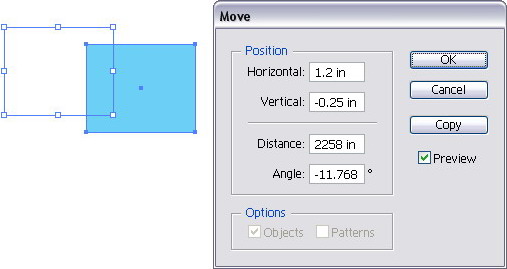
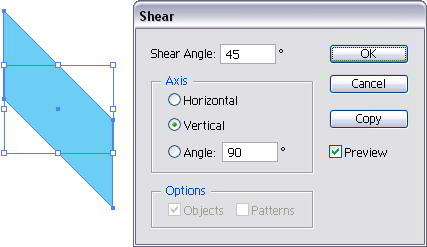
 (dialog box appear), set the axis value.
(dialog box appear), set the axis value.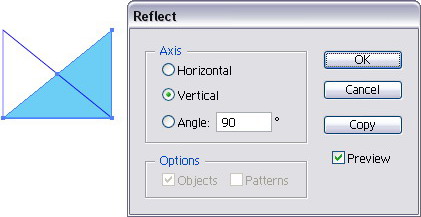
 start shear by click & drag outside area of the object, the object will follow mouse direction.
start shear by click & drag outside area of the object, the object will follow mouse direction.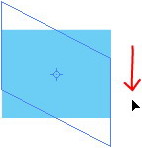 Use your cursor direction where you want the Shear direction to follow.
Use your cursor direction where you want the Shear direction to follow.